Discover METRICS that MATTER
T1D TRIAL
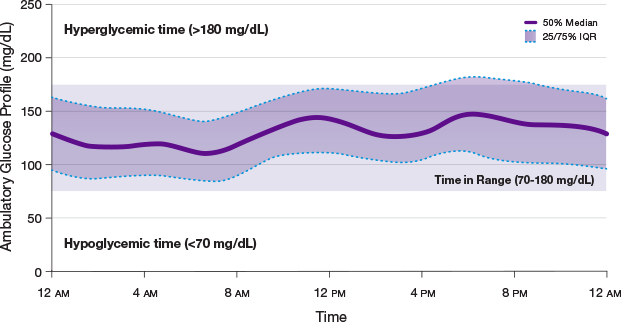
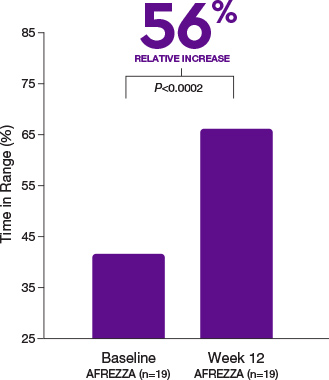
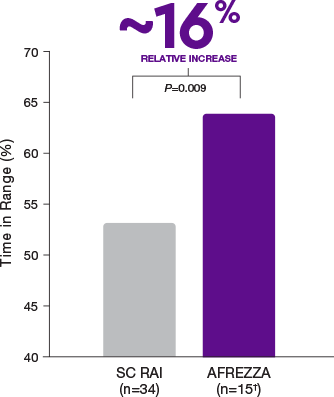
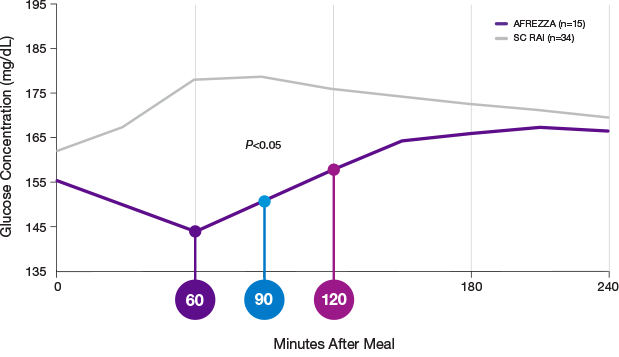
AFFINITY-1
AFREZZA effectively lowers A1C1,2
In the AFFINITY-1 pivotal T1D trial, patients treated with AFREZZA and patients treated with SC RAI achieved similar average A1C reductions from baseline. Baseline A1C levels were 7.94% for patients treated with AFREZZA and 7.92% for patients using SC RAI. By Week 24, AFREZZA reduced A1C to 7.73% (-0.21%), and SC RAI to 7.52% (-0.40%), resulting in a between-group difference of 0.19%
Data from an open-label, non-inferiority trial compared the change in A1C from baseline to Week 24 of prandial AFREZZA (n=174) with that of SC RAI (n=170), both with basal insulin, in adult patients (≥18 years) with T1D and A1C of 7.5% to 10%. AFREZZA provided less A1C reduction than RAI, satisfied the non-inferiority margin of 0.4%, and the difference was statistically significant. More subjects in the SC RAI group achieved the A1C target of ≤7%.1
T2D TRIAL
AFFINITY-2
AFREZZA significantly decreased A1C levels in inadequately controlled patients on oral agents2,3*
In the AFFINITY-2 pivotal T2D trial, treatment with AFREZZA plus OADs provided a mean reduction in A1C that was statistically significantly greater compared with the A1C reduction observed in the placebo plus OADs group. Baseline A1C levels were 8.25% for patients treated with AFREZZA plus OADs and 8.27% for patients using placebo plus OADs. By Week 24, AFREZZA reduced A1C by 0.82% compared with 0.42% in the placebo group, resulting in a between-group difference of 0.4% (P<0.0001). Additionally, 32% of AFREZZA-treated subjects achieved an A1C of ≤7%, compared with 15% in the placebo group
Data from a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in insulin-naïve patients with T2D whose disease was inadequately controlled with optimal/maximal-tolerated doses of OADs. After a 6-week run-in period, patients were randomized to receive either AFREZZA plus OADs (n=177) or inhaled (placebo) powder without insulin plus OADs (n=176).3
*Inadequately controlled patients included those whose A1C was ≥7.5% to ≤10%.