New FDA approved starting dose for patients switching from SC RAI1
Patients with T1D or T2D switching from SC RAI
- Starting: Convert each injected mealtime insulin dose or bolus dose for patients using insulin pumps by multiplying the SC RAI units by 2X to achieve comparable effect of AFREZZA dose (up to 16 AFREZZA UNITS); round the AFREZZA UNITS down to the closest cartridge size resulting in ~2X SC RAI dosing1-3
Calculate starting dose
Enter current SC RAI units
By using this resource, you agree to the following: This Dosing Calculator is being provided "AS IS" and is intended for use only by qualified healthcare providers. All calculations should be confirmed before use. MannKind makes no claims as to the accuracy of the information contained herein. Neither MannKind, nor any other party involved in the preparation or publication of this site, shall be liable to you or others for any decisions made or actions taken by you or others in reliance on this information.
References: 1. Bode BW, McGill JB, Lorber DL, Gross JL, Chang PC, Bregman DB. Inhaled Technosphere insulin compared with injected prandial insulin in type 1 diabetes: a randomized 24-week trial. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(12):2266–2273. 2. Akturk HK, Snell-Bergeon JK, Rewers A, et al. Improved postprandial glucose with inhaled Technosphere insulin compared with insulin aspart in patients with type 1 diabetes on multiple daily injections: the STAT study. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2018;20(10):639–647.
Please note this calculator does not substitute or overwrite medical judgment.
Correction and titration
- Correct: Add correction doses as needed based on postmeal blood glucose level
Mealtime correction doses at 1 and/or 2 hours postmeal4

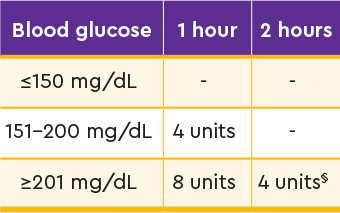
§2-hour correction used only if BG is ≥201 mg/dL and has not decreased by ≥50 mg/dL between 1 and 2 hours.
Data from the STAT study of patients with T1D with A1C levels 6.5% to 10%. Individuals were randomized to treatment with titrated AFREZZA (n=22) or titrated SC RAI aspart (n=34) and included in the final analysis. All were required to wear a real-time CGM throughout the trial. Patients in the AFREZZA group were advised to take supplemental inhalations at 1 and 2 hours after meals if indicated based on PPG values.4
- Titrate: Like all insulin therapy, monitor therapeutic effect of AFREZZA and adjust dosing as needed to achieve optimal glycemic control1
AFREZZA delivers flexible options

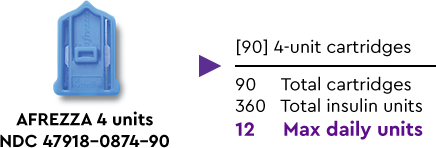
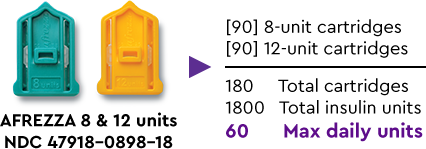



A1C=glycated hemoglobin; CGM=continuous glucose monitoring; EMR=electronic medical records; PPG=postprandial glucose; SC RAI=subcutaneous rapid acting insulin; T1D=type 1 diabetes; T2D=type 2 diabetes.
© MannKind Corporation January 2026. US-AFR-2737

