physiologic insulin
ultra-rapid delivery1,2
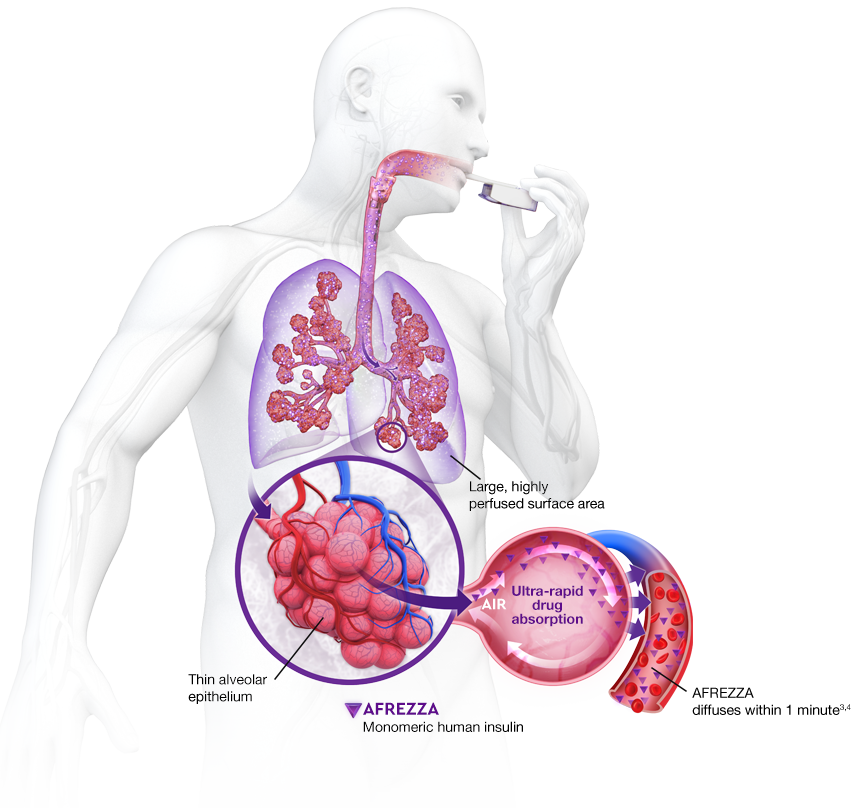
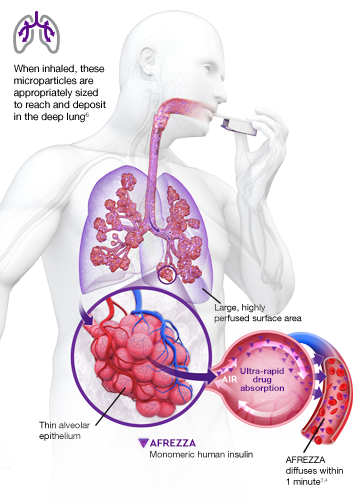



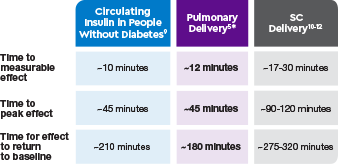
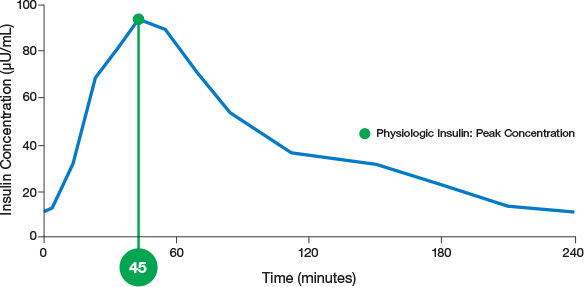
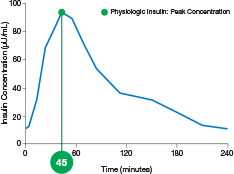
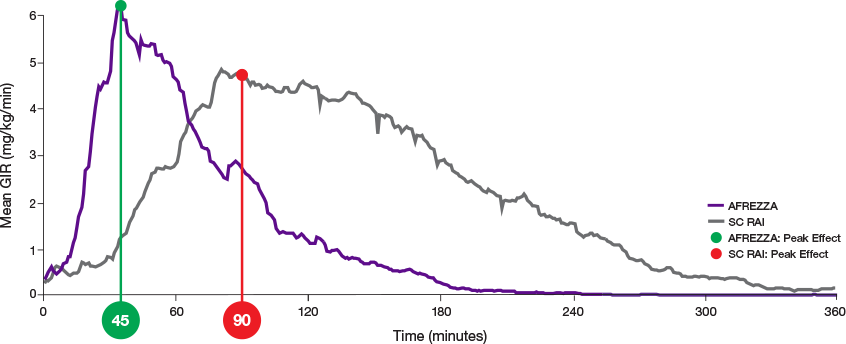
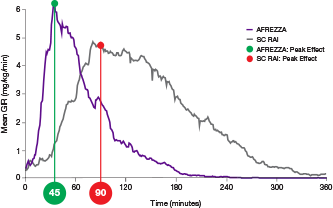
AUC=area under curve; GIR=glucose infusion rate; MGTT=mean glucose tolerance test; PK=pharmacokinetics; PD=pharmacodynamics; RAI=rapid-acting insulin; SC RAI=subcutaneous rapid-acting insulin; T1D=type 1 diabetes.
References: 1. Heinemann L, Baughman R, Boss A, Hompesch M. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of a novel inhaled insulin. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017;11(1):148-156. 2. Heinemann L, Parkin CG. Rethinking the viability and utility of inhaled insulin in clinical practice. J Diabetes Res. 2018:4568903. doi: 10.1155/2018/45689 3. Data on file. MannKind Corporation. 4. Grant M, Harris E, Leone-Bay A, Rousseau K. Poster presented at: Diabetes Technology Society Meeting; November 2-4, 2006; Atlanta, GA. 5. Afrezza (insulin human) Inhalation Powder Prescribing Information. MannKind Corporation. 6. Leone-Bay A, Baughman R, Smutney C, Kocinsky J. Innovation in drug delivery by inhalation. OnDrugDelivery Magazine. 2010;4-8. 7. Sarala N, Bengalorkar G, Bhuvana K. Technosphere: new drug delivery system for inhaled insulin. Fut Prescriber. 2012;13:14-16. https://doi.org/10.1002/fps.90 8. Rave K, Heise T, Heinemann L, Boss AH. Inhaled Technosphere insulin in comparison to subcutaneous regular human insulin: time action profile and variability in subjects with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2008;2(2):205-212. 9. Caumo A, Bergman RN, Cobelli C. Insulin sensitivity from meal tolerance tests in normal subjects: a minimal model index. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(11):4396-4402 10. Grant M, Heise T, Baughman R. Comparison of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of inhaled technosphere insulin and subcutaneous insulin Lispro in the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022;61(3):413-422. doi:10.1007/s40262-021-01084-0 11. Fiasp (insulin aspart injection) Prescribing Information. Novo Nordisk. 12. Lyumjev (insulin lispro-aabc injection) Prescribing Information. Eli Lilly and Company.
© MannKind Corporation January, 2025. US-AFR-2598
Afrezza® (insulin human) Inhalation Powder is a rapid acting inhaled human insulin indicated to improve glycemic control in adult patients with diabetes mellitus.
Limitations of Use: Not recommended for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis, not recommended in patients who smoke or have recently stopped smoking.
WARNING: RISK OF ACUTE BRONCHOSPASM IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE. Acute bronchospasm has been observed in patients with asthma and COPD using AFREZZA. AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients with chronic lung disease such as asthma or COPD. Before initiating AFREZZA, perform a detailed medical history, physical examination, and spirometry (FEV1) to identify potential lung disease in all patients.